Description
Introduction
Kanban is a popular workflow management method that helps teams visualize work, optimize flow, and enhance collaboration. Originally developed for manufacturing, it has become a core principle in Agile project management due to its flexibility, simplicity, and ability to continuously improve team productivity. This course provides a comprehensive introduction to Kanban fundamentals, emphasizing its principles and practical implementation in managing work for Agile teams.
Whether you’re new to Agile or looking to refine your team’s workflow, learning Kanban will enable you to create efficient, manageable processes that reduce waste, minimize delays, and focus on delivering high-quality results. By understanding Kanban, teams can improve the transparency of their work, make better decisions, and continuously improve their processes.
Prerequisites
- Basic knowledge of Agile methodology.
- Familiarity with project management concepts.
- No prior Kanban experience required.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Kanban
1.1 What is Kanban?
1.2 History and Origins of Kanban
1.3 Benefits of Implementing Kanban
1.4 Kanban vs. Other Agile Methodologies (e.g., Scrum)
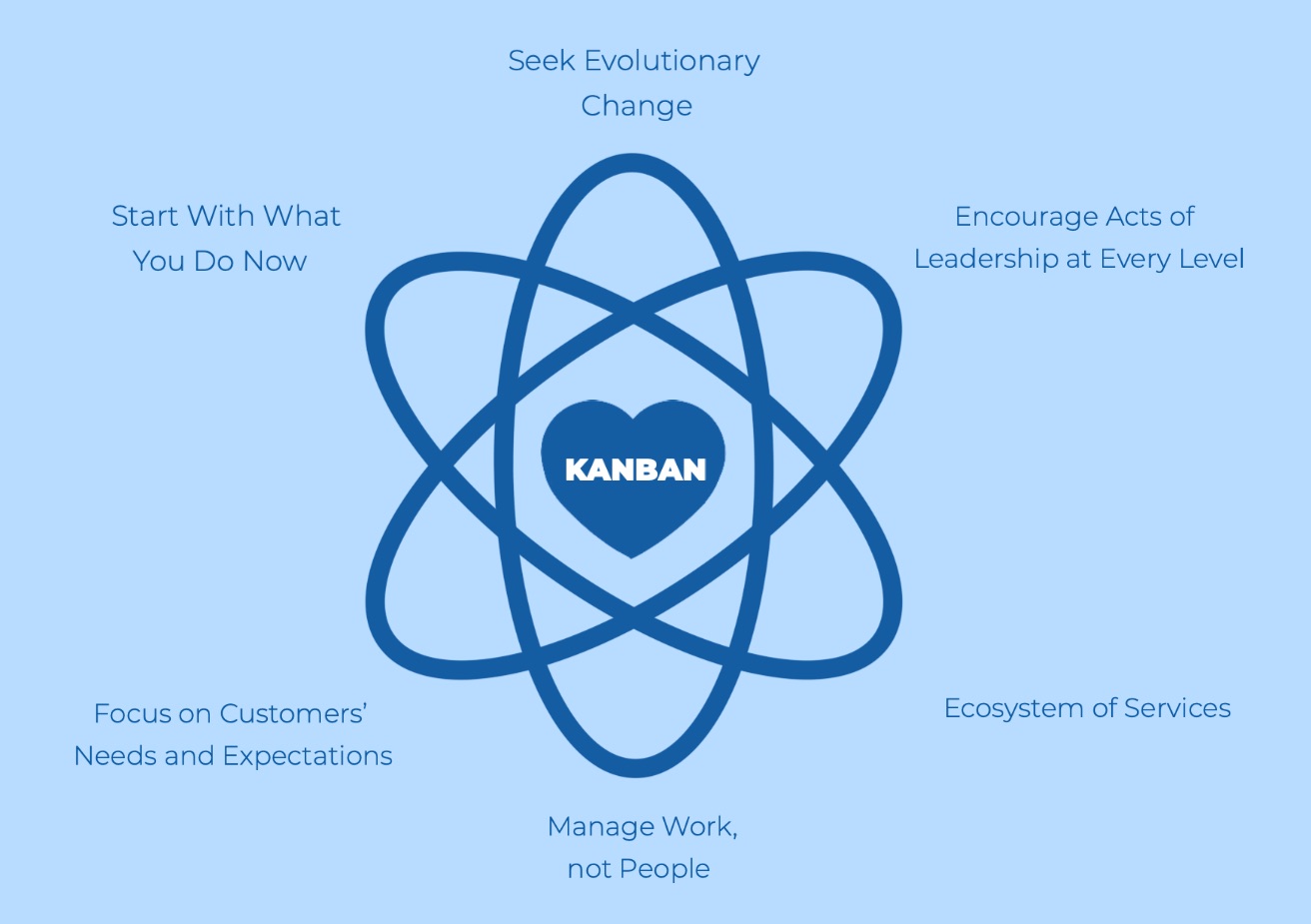
1.5 Key Principles of Kanban - Core Principles of Kanban
2.1 Visualizing Work
2.2 Limiting Work in Progress (WIP)
2.3 Managing Flow
2.4 Making Process Policies Explicit
2.5 Implementing Feedback Loops
2.6 Improving Collaboratively, Evolving Experimentally - Kanban Board Setup and Design
3.1 Types of Kanban Boards (Physical vs. Digital)
3.2 Key Components of a Kanban Board
3.3 Defining Workflow States and Columns
3.4 Kanban Board Best Practices
3.5 Digital Kanban Tools and Platforms - Work Item Types and Workflow Management
4.1 Defining Work Items (e.g., Tasks, Features, Bugs)
4.2 Managing Different Types of Work
4.3 Prioritizing and Categorizing Work Items
4.4 Tracking Progress and Movement through Workflow
4.5 Handling Blockers and Bottlenecks - Work in Progress (WIP) Limits
5.1 Importance of WIP Limits in Kanban
5.2 Setting Effective WIP Limits
5.3 Benefits of WIP Limits in Reducing Multitasking
5.4 How WIP Limits Improve Flow and Focus
5.5 Managing WIP in Complex Teams and Projects - Flow and Continuous Delivery
6.1 Optimizing the Flow of Work through the System
6.2 Identifying and Removing Bottlenecks(Ref: Mastering PRINCE2: A Comprehensive Guide to Project Management)
6.3 Cycle Time and Lead Time: Key Metrics for Flow
6.4 Continuous Delivery and Improvement in Kanban
6.5 Kaizen: The Japanese Principle of Continuous Improvement - Metrics and Measurements in Kanban
7.1 Key Kanban Metrics: Cycle Time, Throughput, and Lead Time
7.2 Understanding Flow Efficiency
7.3 Measuring Team Performance with Cumulative Flow Diagrams
7.4 Using Metrics to Make Data-Driven Decisions
7.5 Tracking and Reporting Progress - Implementing Kanban in Agile Teams
8.1 Getting Started with Kanban in Your Team
8.2 Transitioning from Scrum to Kanban
8.3 Defining Roles in a Kanban System
8.4 Aligning Kanban with Business Goals and Strategy
8.5 Managing Distributed Teams with Kanban - Improving Collaboration with Kanban
9.1 Promoting Transparency and Accountability
9.2 Enhancing Communication Among Team Members
9.3 Facilitating Cross-Functional Collaboration
9.4 Creating a Culture of Continuous Improvement
9.5 Running Effective Kanban Meetings - Scaling Kanban for Larger Teams and Projects
10.1 Managing Multiple Teams with Kanban
10.2 Scaling Kanban for Program and Portfolio Management
10.3 Coordinating Across Teams and Workflows
10.4 Integrating Kanban with Other Agile Frameworks (e.g., SAFe)
10.5 Overcoming Challenges in Scaling Kanban - Kanban Best Practices and Common Pitfalls
11.1 Best Practices for Successful Kanban Implementation
11.2 Common Challenges Teams Face with Kanban
11.3 How to Overcome Pitfalls in Kanban Systems
11.4 Continuous Improvement and Iteration in Kanban
11.5 Lessons Learned from Successful Kanban Teams - Conclusion
12.1 Recap of Key Kanban Concepts
12.2 The Value of Visualizing and Managing Work
12.3 Kanban as a Tool for Continuous Improvement
12.4 Moving Forward: Implementing Kanban in Your Own Team
12.5 Additional Resources and Tools for Kanban Mastery
Conclusion
Kanban is an indispensable methodology for managing and optimizing workflows, especially in Agile environments. By focusing on the visualization of work, limiting WIP, and continuously improving processes, Kanban enables teams to deliver more efficiently and with higher quality. Its flexibility and simplicity make it suitable for teams of all sizes, whether working on simple tasks or large, complex projects.
By mastering Kanban Fundamentals for Agile Teams, teams can reduce bottlenecks, improve communication, and ultimately enhance their ability to respond to changing priorities and deliver value faster. The principles and practices you’ve learned in this course will help you streamline workflows and foster a culture of continuous improvement within your team, making Kanban a powerful tool for any Agile practitioner.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.