Description
Introduction
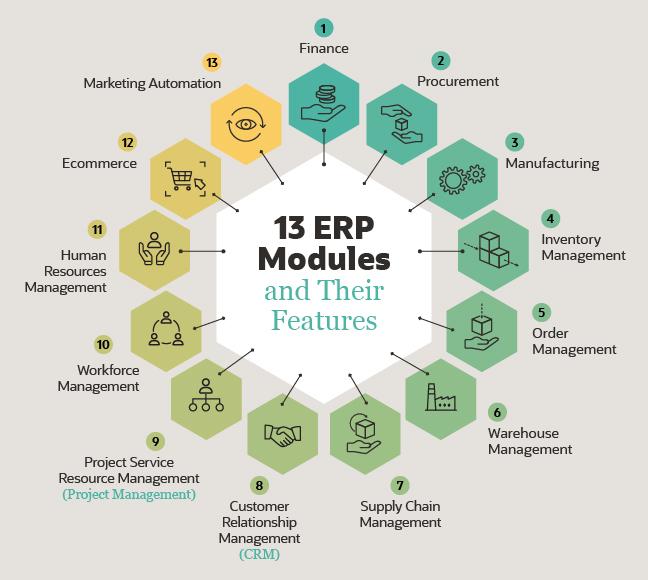
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are integral tools for businesses seeking to streamline their processes and achieve operational efficiency. ERP integrates various core business functions, such as finance, human resources, supply chain management, and customer relationship management, into a unified system. This integration ensures better coordination, real-time data accessibility, and improved decision-making.
This course, Enterprise Resource Planning Essentials: Streamlining Business Processes, offers a comprehensive introduction to ERP systems. Participants will learn how to optimize business operations, reduce redundancies, and enhance data visibility across departments using ERP solutions. Whether you’re new to ERP or seeking to improve your current system, this course will equip you with the essential knowledge needed to understand and implement ERP effectively in modern businesses.
Prerequisites
- Basic understanding of business processes and operations.
- Familiarity with general information technology concepts.
- No prior ERP knowledge is required, though exposure to business software tools is helpful.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to ERP Systems
1.1 What is ERP?
1.2 Evolution and History of ERP Systems
1.3 The Benefits of ERP Systems in Business
1.4 Key Features of ERP Systems
1.5 Types of ERP Solutions - Core Components of ERP Systems
2.1 Financial Management
2.2 Human Resource Management (HRM)
2.3 Supply Chain Management (SCM)
2.4 Manufacturing and Production Management
2.5 Customer Relationship Management (CRM) - The ERP Implementation Process
3.1 Pre-Implementation Planning
3.2 Customization and Configuration
3.3 Data Migration and Integration
3.4 Testing and Deployment
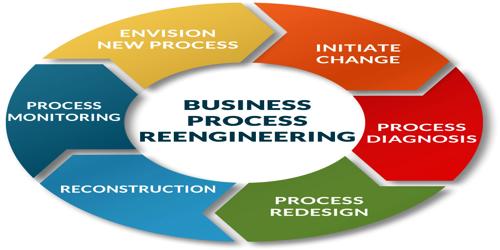
3.5 Post-Implementation Support - Business Process Optimization with ERP
4.1 Identifying Business Process Gaps
4.2 Mapping Processes to ERP Functions
4.3 Streamlining Operations Across Departments
4.4 Automating Repetitive Tasks
4.5 Improving Decision-Making with Real-Time Data - Choosing the Right ERP Solution
5.1 ERP Software Selection Criteria
5.2 On-Premise vs. Cloud ERP
5.3 Top ERP Vendors (SAP, Oracle, Microsoft, etc.)
5.4 Cost Analysis and Budgeting
5.5 Vendor Evaluation and Negotiation - Configuring and Customizing ERP Systems
6.1 Setting Up Core Modules (Finance, HR, SCM, etc.)
6.2 Managing User Access and Permissions
6.3 Customizing ERP for Unique Business Needs
6.4 Ensuring Data Security and Integrity
6.5 Reporting and Analytics Features - Cloud ERP vs. On-Premise ERP
7.1 Understanding Cloud ERP
7.2 Advantages of Cloud ERP
7.3 Considerations for On-Premise ERP
7.4 Hybrid ERP Solutions
7.5 Cloud ERP Implementation Challenges - Integrating ERP with Other Business Applications
8.1 ERP Integration with Third-Party Software
8.2 Middleware and API Integration Tools
8.3 Cross-Platform Data Sharing and Consistency
8.4 Managing Data Flow Between Systems
8.5 Best Practices for ERP System Integration - ERP for Specific Business Functions
9.1 ERP for Financial Management and Accounting
9.2 ERP for Supply Chain and Inventory Control
9.3 ERP for Sales and Marketing Automation
9.4 ERP for Human Resources and Payroll(Ref: Sage CRM Systems Admin: Advanced Features and Management)
9.5 ERP for Manufacturing and Production Management - Performance Management and Reporting in ERP
10.1 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
10.2 Real-Time Dashboards and Reporting
10.3 Business Intelligence Features in ERP
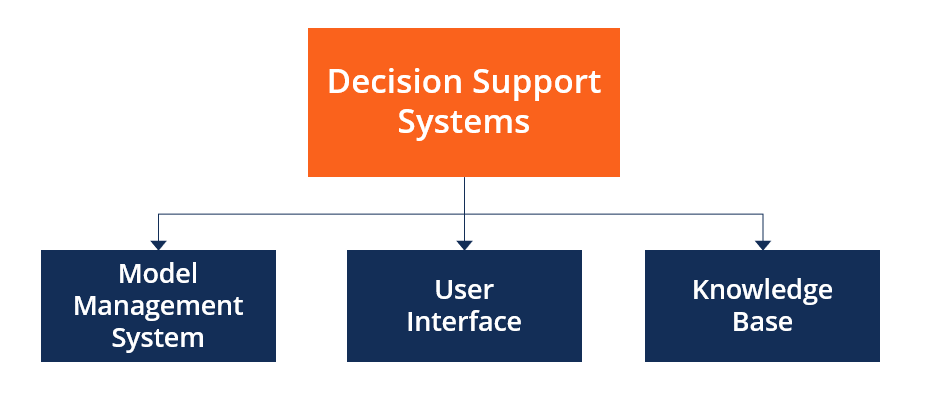
10.4 Advanced Analytics and Decision Support
10.5 Visualizing Data for Actionable Insights - Future Trends in ERP Systems
11.1 The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on ERP
11.2 The Role of Big Data and ERP Systems
11.3 Cloud ERP and the Rise of SaaS
11.4 Mobile ERP Applications
11.5 ERP in the Age of Industry 4.0 - Case Studies in ERP Implementation
12.1 Case Study: ERP in Manufacturing
12.2 Case Study: ERP in Retail
12.3 Case Study: ERP for Service-Oriented Businesses
12.4 Case Study: Cloud ERP for Small Enterprises
12.5 Case Study: ERP for Healthcare - ERP Troubleshooting and Best Practices
13.1 Identifying Common ERP Challenges
13.2 Troubleshooting System Performance Issues
13.3 Managing User Adoption and Training
13.4 Keeping ERP Systems Updated
13.5 Best Practices for ERP Maintenance and Support - Certification and Career Pathways in ERP
14.1 ERP Certifications and Qualifications
14.2 Career Paths in ERP Implementation and Support
14.3 Skills for ERP Professionals
14.4 Networking and Career Advancement Opportunities
14.5 Continuing Education in ERP
Conclusion
The Enterprise Resource Planning Essentials: Streamlining Business Processes course will provide you with a thorough understanding of ERP systems and their role in transforming business operations. By integrating core business functions, ERP systems provide organizations with real-time visibility, improved data accuracy, and streamlined workflows. This course equips you with the knowledge to choose, implement, and optimize ERP solutions tailored to business needs.
With a focus on practical applications, real-world case studies, and emerging trends in ERP technologies, you will be prepared to leverage ERP systems to enhance efficiency, reduce operational costs, and improve decision-making. Whether you’re looking to enhance your career in ERP or implement ERP in your organization, this course provides the foundational skills necessary to excel in the evolving world of business technology.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.