1: Introduction to Test-Driven Development (TDD)
1.1 Overview of TDD: Definition and Benefits
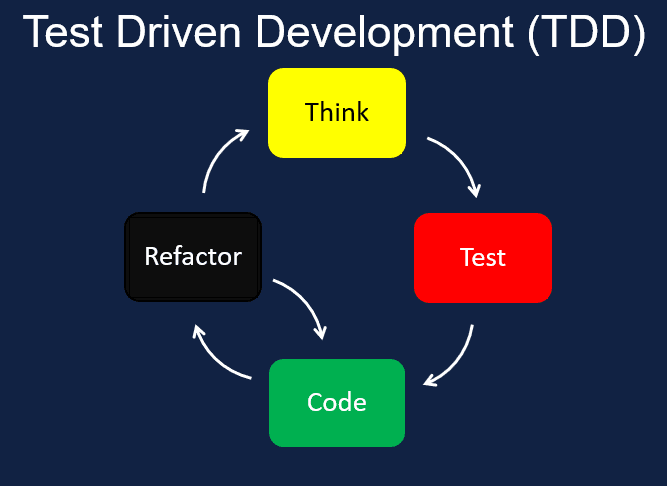
1.2 The TDD Workflow: Red, Green, Refactor
1.3 The Role of TDD in Agile Development
1.4 Understanding Unit Tests and Test Automation
2: Writing Effective Unit Tests
2.1 Principles of Writing Good Tests: AAA (Arrange, Act, Assert)
2.2 Choosing What to Test: Positive and Negative Scenarios
2.3 Introduction to Testing Frameworks
2.3.1 JUnit
2.3.2 NUnit
2.3.3 PyTest
2.4 Writing the First Test: Red Phase
3: Implementing Code to Pass Tests
3.1 Writing Minimal Code to Make the Test Pass: Green Phase
3.2 Balancing Functionality with Test Satisfaction
3.3 Avoiding Overengineering During the Initial Coding Phase
3.4 Code and Test Iteration Process (Ref: Manual Testing Essentials: Techniques and Processes)
4: Refactoring Code for Clean Design
4.1 Identifying Code Smells
4.2 Refactoring Techniques for Simplifying Code
4.3 Ensuring Code Maintainability and Reusability
4.4 The Role of Refactoring in Continuous Improvement
5: TDD in an Agile Workflow
5.1 Integrating TDD with Agile Principles
5.1.1 Scrum
5.1.2 Kanban
5.2 Continuous Integration (CI) and Test Automation
5.3 Leveraging TDD for Short Iteration Cycles and Feedback Loops
5.4 Collaboration Between Developers, Testers, and Product Owners
6: Advanced TDD Techniques
6.1 Parameterized and Data-Driven Tests
6.2 Using Mocks, Stubs, and Fakes for Testing Dependencies
6.3 Testing Legacy Code and Refactoring it to TDD
6.4 Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) vs. TDD: Key Differences
7: Test-Driven Development for Different Architectures
7.1 TDD for Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
7.2 TDD for Functional Programming
7.3 TDD for Web Applications, APIs, and Microservices
7.4 TDD in Continuous Delivery Pipelines
8: Common TDD Challenges and Solutions
8.1 Dealing with Long-Running Tests and Performance Bottlenecks
8.2 Handling Complex Business Logic in TDD
8.3 Overcoming the Fear of Refactoring
8.4 Mitigating Technical Debt through Continuous Testing
9: Best Practices for TDD
9.1 Writing Maintainable Tests
9.2 Striking the Right Balance Between Testing and Coding
9.3 Avoiding Test Overhead and Maintaining Test Efficiency
9.4 Code Reviews and Pair Programming in TDD
10: TDD Tools and Frameworks
10.1 Popular TDD Tools for Different Languages
10.1.1 JUnit
10.1.2 xUnit
10.1.3 Mocha
10.2 Integrating TDD into Build Pipelines
10.2.1 Maven
10.2.2 Gradle
10.3 Using Continuous Integration Tools
10.3.1 Jenkins
10.3.2 GitLab
10.3.3 Travis CI
10.4 Debugging and Troubleshooting TDD Code
11: TDD for Teams: Collaboration and Culture
11.1 Creating a TDD-Driven Culture in Agile Teams
11.2 Collaboration Between Developers and QA in TDD
11.3 Using TDD to Foster Better Communication and Code Quality
11.4 Measuring and Improving Test Coverage
12: Final Project: TDD in Action
12.1 Building a Complete Application Using TDD
12.2 Implementing Tests, Code, and Refactoring Iteratively
12.3 Integrating the TDD Process into a Continuous Integration Workflow
12.4 Final Presentation of Results and Code Review






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.