Description
Introduction of Cloud Infrastructure Fundamentals
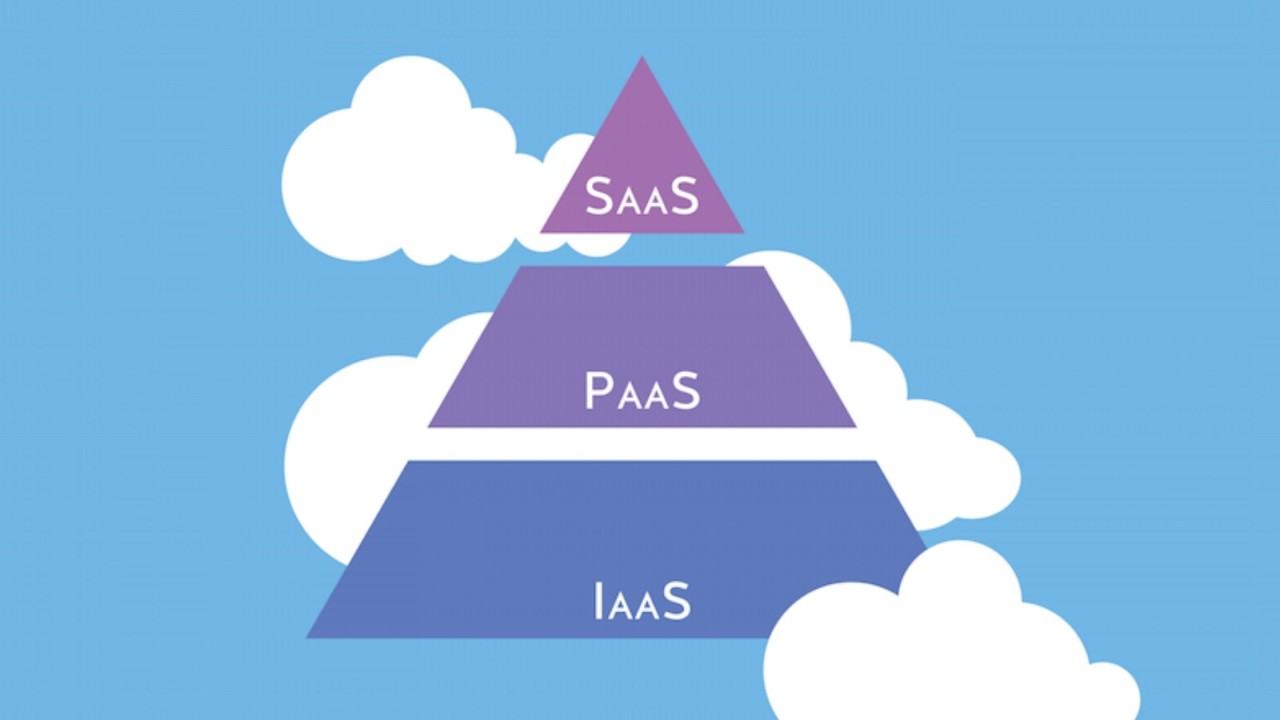
Cloud computing offers scalable, on-demand access to a variety of computing resources, allowing businesses to operate more efficiently and reduce costs. The three main service models—Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS)—each provide different levels of abstraction and management responsibilities. This course will explore these three core cloud service models in detail, helping you understand their differences, use cases, and when to adopt each model.
Prerequisites
- Basic knowledge of computing and IT concepts.
- Familiarity with internet technologies, networking, and virtualization concepts is beneficial but not mandatory.
- No prior cloud computing experience is required.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Cloud Computing
1.1 What is Cloud Computing?
1.2 Evolution and Adoption of Cloud Services
1.3 Benefits of Cloud Computing
1.4 Overview of Service Models - Understanding IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
2.1 What is IaaS?
2.2 Key Components of IaaS: Compute, Storage, Networking
2.3 IaaS Providers and Popular Platforms (e.g., AWS EC2, Azure VMs, Google Compute Engine)
2.4 Use Cases for IaaS: Virtualization, Hosting, Scalability
2.5 Pros and Cons of IaaS - Understanding PaaS (Platform as a Service)
3.1 What is PaaS?
3.2 Key Components of PaaS: Development Tools, Middleware, Databases
3.3 Popular PaaS Providers (e.g., Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Services, Heroku)
3.4 Use Cases for PaaS: Application Development and Deployment
3.5 Pros and Cons of PaaS - Understanding SaaS (Software as a Service)
4.1 What is SaaS?
4.2 Key Features of SaaS: Subscription-Based, Access Over the Internet
4.3 Popular SaaS Providers (e.g., Google Workspace, Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365)
4.4 Use Cases for SaaS: Collaboration, CRM, Enterprise Applications
4.5 Pros and Cons of SaaS - Comparing IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
5.1 Key Differences Between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
5.2 Choosing the Right Model for Your Needs
5.3 Case Studies: Real-World Examples of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS in Action
5.4 Benefits of Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies - Managing and Securing Cloud Infrastructure
6.1 Cloud Security: Key Considerations(Ref: Introduction to Cloud Computing: Basics and Best Practices)
6.2 Best Practices for Securing IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS Environments
6.3 Cloud Governance and Compliance Challenges
6.4 Monitoring and Managing Cloud Resources - Cloud Economics and Cost Management
7.1 Understanding Cloud Pricing Models
7.2 Cost Optimization in IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
7.3 Managing Cloud Budgets and Reducing Wastage
7.4 Forecasting and Managing Long-Term Costs - Future Trends in Cloud Infrastructure Fundamentals
8.1 Innovations in IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
8.2 The Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Automation in Cloud Services
8.3 The Role of Edge Computing and Hybrid Clouds in Future Architectures
8.4 Cloud Computing in Emerging Technologies (IoT, Blockchain, etc.)
Conclusion
Understanding the differences and applications of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS is crucial for businesses and IT professionals looking to leverage cloud computing effectively. Each model offers unique advantages depending on the organization’s needs, from raw infrastructure with IaaS to fully managed applications with SaaS. By understanding these cloud models, their use cases, and how to manage them efficiently, organizations can make informed decisions about which cloud solutions best support their business objectives while optimizing performance, cost, and security.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.